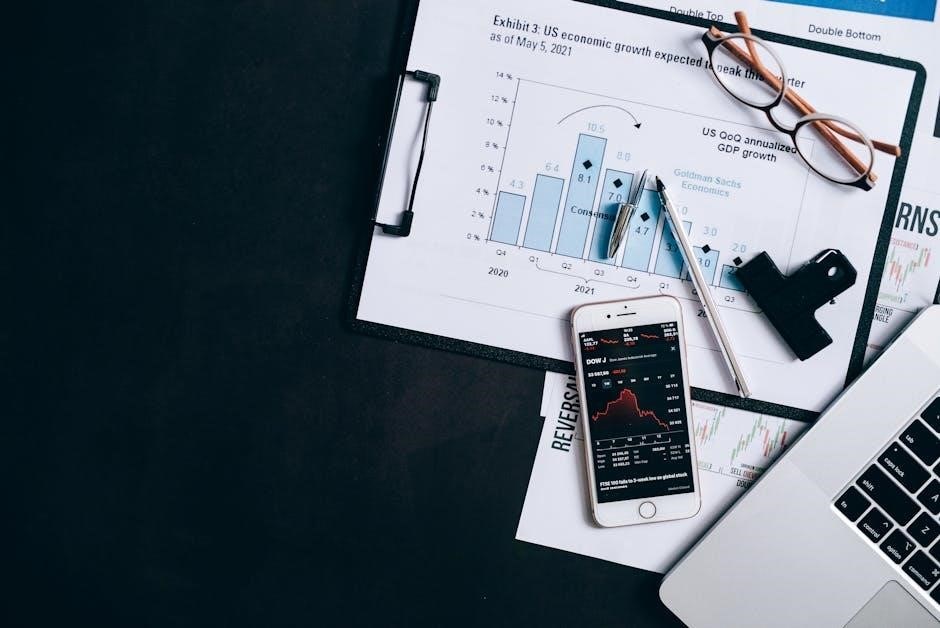

Stock Investing For Dummies provides a comprehensive guide for beginners, simplifying complex concepts and offering practical advice to build wealth through informed decisions.
What is Stock Investing?
Stock investing involves buying shares of companies, becoming a partial owner, and earning returns through dividends or capital appreciation. It allows individuals to benefit from a company’s growth and profits, making it a key strategy for long-term financial growth and wealth creation.
Why Stock Investing is Important for Financial Growth
Stock investing is a powerful tool for building wealth over time, offering potential for higher returns than traditional savings accounts. It allows individuals to own a part of companies, benefiting from their growth and profits. By leveraging the stock market, investors can achieve long-term financial goals, such as retirement or buying a home, while learning to make informed decisions to secure their financial future.

Understanding the Basics of the Stock Market
The stock market enables buying and selling of company shares, allowing businesses to raise capital and investors to participate in economic growth and wealth creation.
How Stocks Work
Stocks represent ownership in a company, allowing investors to benefit from its profits and growth. When you buy shares, you become a partial owner, potentially earning dividends or selling at a higher price for profit. Stocks are traded on exchanges, providing liquidity and opportunities to build wealth over time through informed investments.
Key Terms Every Beginner Should Know
Understanding key terms is essential for making informed decisions. A portfolio is a collection of investments like stocks and bonds. Dividends are payments from companies to shareholders. A bull market refers to rising trends, while a bear market indicates declines. An IPO is the first public offering of a company’s stock. These terms are fundamental for navigating the stock market effectively.

Assessing Your Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Evaluate your financial objectives and risk tolerance to align your investments with your goals and comfort level with market volatility.
Setting Realistic Financial Goals
Define clear financial objectives, such as retirement savings or buying a home, and assess your time horizon and risk tolerance. Evaluate your current debt, tax situation, and insurance coverage to create a solid foundation. Start with low-risk investments and gradually adjust as you gain confidence. Seek guidance from resources like Investing For Dummies to ensure your goals are achievable and aligned with your financial situation.
Understanding Risk Tolerance in Stock Investing
Assess your comfort with market volatility to determine your risk tolerance. Consider your financial obligations, debt, and ability to withstand losses. Investors with higher risk tolerance may opt for growth stocks, while those preferring stability might choose dividend-paying stocks; Evaluate your goals and time horizon to align your investments with your risk appetite, as advised in resources like Investing For Dummies.

Types of Stocks and Investment Strategies
Stocks include growth, dividend, and value stocks, each offering unique benefits. Investment strategies range from passive, long-term approaches to active trading, tailored to individual goals and risk tolerance.
Different Types of Stocks (Growth, Dividend, Value)
Growth stocks are shares in companies expected to grow faster than others, often reinvesting profits. Dividend stocks provide regular income through payouts. Value stocks are undervalued relative to metrics like P/E ratio. Each type appeals to different investment goals and risk profiles, offering unique benefits for growth, income, or capital appreciation opportunities.
Passive vs. Active Investing
Passive investing involves buying and holding assets like index funds, mirroring market performance with minimal effort. Active investing requires frequent buying and selling to outperform the market. Passive suits long-term goals with lower fees, while active demands time and expertise. Beginners often start with passive due to its simplicity and lower costs, aligning with resources like “Stock Investing For Dummies” and Investopedia guides.

Fundamental Analysis for Beginners
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company’s financial statements and market position to assess its investment potential, helping beginners make informed decisions with resources like “Stock Investing For Dummies.”
How to Read Financial Statements
Reading financial statements involves analyzing income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. “Stock Investing For Dummies” guides beginners to interpret these documents, understand revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flows. This helps in assessing a company’s financial health and making informed investment decisions. Clear explanations simplify complex terms, empowering new investors to evaluate stocks effectively and confidently.
Evaluating Companies Before Investing
Evaluating companies involves assessing their financial health, debt levels, revenue growth, and competitive position. “Stock Investing For Dummies” recommends analyzing income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to gauge profitability and stability. Investors should also consider market trends, industry strength, and management quality before making informed decisions. This step ensures aligning investments with personal financial goals and risk tolerance.
Getting Started with Stock Investing
Begin your journey with resources like Stock Investing For Dummies, which offers clear guidance for newcomers. Start by understanding the basics, assessing your financial goals, and choosing a reliable brokerage account to begin trading confidently.
Choosing the Right Brokerage Account
Selecting the right brokerage account is crucial for beginners. Look for platforms with low fees, user-friendly interfaces, and excellent customer support. Consider accounts that offer educational resources, such as tutorials and webinars, to help you learn. Popular options include Fidelity, Ameritrade, and Vanguard. Ensure the broker aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance to create a solid foundation for your investing journey.
How to Place Your First Trade
Placing your first trade involves selecting a stock, deciding on the type of order, and executing it through your brokerage account. Start by researching a company and using tools like limit or market orders. Ensure you understand the fees and risks involved. Practice with a paper trading account if available, and take your time to make informed decisions to build confidence in your trading skills.

Common Mistakes to Avoid for Beginners
Beginners often make costly errors like overtrading, emotional decision-making, and ignoring diversification. Avoid these pitfalls by setting clear goals, staying disciplined, and educating yourself continuously to ensure long-term success.
Overtrading and Emotional Decision-Making
Overtrading and emotional decision-making are common pitfalls for beginners. Overtrading leads to excessive fees and poor outcomes, while emotions like fear and greed can cloud judgment. Stay disciplined by setting clear goals and avoiding impulsive actions. Use tools like stop-loss orders to manage risk and reduce emotional influence. Educate yourself to make informed, rational decisions rather than reacting to short-term market fluctuations.
The Pitfalls of Ignoring Diversification
Ignoring diversification is a critical mistake, as it exposes investors to heightened risk. Placing all investments in a single stock or sector can lead to significant losses if that area underperforms. Diversification spreads risk across various industries and asset types, reducing vulnerability to market volatility; Beginners should aim for a balanced portfolio to protect capital and enhance potential returns over time.

Resources for Learning Stock Investing
Stock Investing For Dummies and Dummies.com offer practical guidance. Investopedia provides educational tools, helping beginners build a strong foundation in stock market investing effectively and confidently.
Recommended Books for Beginners
Stock Investing For Dummies by Paul Mladjenovic is a top choice, offering clear, practical guidance for newcomers. It covers essential topics like financial statements, risk management, and portfolio building. Ranked as a top resource by Barron’s, this book provides a solid foundation for understanding the stock market and making informed decisions. Perfect for those looking to start their investing journey with confidence and clarity.
Online Courses and Tools for Stock Market Education
on Coursera. Tools like Investopedia Academy and Stock Market Simulator offer hands-on learning. Platforms such as Fidelity Learning Center and TD Ameritrade’s Education Center provide free resources, including webinars and tutorials. These tools help build a strong foundation and confidence in stock market investing.

Staying Informed About Market Trends
Stay updated with market trends using reliable sources like Investopedia, Dummies.com, and financial news outlets. Tools like Fidelity and Ameritrade offer real-time data and educational resources for beginners.
How to Follow Market News
To stay informed, follow financial news through reliable sources like Investopedia, The Wall Street Journal, and Dummies.com. Set up daily updates and alerts for market trends, earnings reports, and economic indicators. Utilize brokerage platforms like Fidelity and Ameritrade for real-time data. Additionally, explore resources like Stock Investing For Dummies by Paul Mladjenovic for practical insights and guidance tailored for beginners.
Using Stock Market Indexes for Guidance
Stock market indexes like the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average serve as key indicators of market health. They help investors gauge overall performance and make informed decisions. By tracking these indexes, beginners can identify trends and align their strategies with broader economic conditions. Stock Investing For Dummies provides detailed insights on leveraging these tools for effective portfolio management and risk assessment.

Building a Long-Term Investment Portfolio
Building a long-term portfolio involves a disciplined approach, focusing on sustainable growth and diversification. Stock Investing For Dummies guides beginners in creating resilient, wealth-building strategies.
Creating a Diversified Portfolio
Creating a diversified portfolio is essential for minimizing risk and maximizing returns. By spreading investments across various sectors, industries, and asset types, beginners can reduce exposure to market volatility. Stock Investing For Dummies recommends balancing growth, dividend, and value stocks. Diversification also includes allocating funds between stocks, bonds, and other securities. Regular portfolio rebalancing ensures alignment with financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Invest in different sectors to avoid concentration risk.
- Balance stock and bond allocations based on risk appetite.
- Rebalance periodically to maintain optimal diversification.
- Rebalance annually or as needed based on market changes.
- Adjust allocations to maintain desired risk levels.
- Align adjustments with long-term financial objectives.
Regular Portfolio Rebalancing
Regular portfolio rebalancing ensures your investments remain aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Over time, market fluctuations can shift your asset allocation, requiring adjustments to restore balance. Stock Investing For Dummies suggests reviewing and rebalancing your portfolio annually or when significant life changes occur. This discipline helps manage risk and maintains a strategic investment approach, fostering long-term financial success. Consistency is key to achieving stability and growth.